1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s here, reshaping industries and redefining the way we work. From the apps we use daily to complex systems in healthcare, finance, and beyond, AI's reach is undeniable. However, with great technological power comes great change. One of the most significant areas AI is transforming is the job market, raising urgent questions about AI and the future of work.
According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2023, AI and machine learning (ML) are driving a wave of job creation across sectors. While the headlines often focus on job losses caused by automation, the report highlights a more balanced reality: for every job made obsolete, new opportunities are emerging. Roles like AI and machine learning specialists, data scientists, and digital transformation experts are set to see explosive growth over the next few years.
Consider this: the report predicts a 40% increase in the number of AI and ML specialists by 2027. Similarly, demand for data analysts, big data experts, and information security analysts will surge by over 30%, creating a combined 2.6 million jobs. This isn’t just a trend—it’s a revolution that requires workers to adapt, learn, and seize the opportunities AI offers.
But not all jobs will thrive in this new landscape. Clerical and secretarial positions, such as bank tellers and data entry clerks, are predicted to decline as automation takes over repetitive tasks. While this may sound daunting, it’s important to note that AI isn’t just about replacing jobs—it’s about enhancing human potential and driving innovation.
At its core, the AI revolution is a call to action. It’s an invitation to upskill, embrace change, and future-proof careers. For software engineers and tech professionals, the time to prepare for AI-driven roles is now. And if you’re aiming for a coveted ML role at a top-tier company, the journey begins with understanding the evolving job market—and equipping yourself with the tools to succeed.
In this blog, we’ll explore the opportunities AI is creating, the industries being reshaped, and the skills you need to thrive in this new era. Let’s dive in and uncover how AI is paving the way for the jobs of tomorrow.
2. The World Economic Forum’s Insights on AI and Jobs
The World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2023 provides a fascinating glimpse into how AI is reshaping the employment landscape. The data reveals not only which roles are in demand but also the broader implications for industries and individuals. Let’s break down the key insights.
A Surge in AI and ML Specialist Roles
The standout projection is a 40% increase in demand for AI and ML specialists by 2027. This translates to tens of thousands of new opportunities in fields such as natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. These specialists are the architects of the AI revolution, designing algorithms, fine-tuning models, and implementing AI solutions across industries.
For tech professionals, this growth signals a clear opportunity to pivot or advance their careers. With the right training and experience, roles like machine learning engineer or AI researcher offer not just lucrative salaries but the chance to work on cutting-edge technologies that shape the future.
The Rising Demand for Data Roles
The report also highlights a 30–35% rise in demand for data-related positions such as:
Data Analysts and Scientists: Professionals who extract actionable insights from vast datasets.
Big Data Specialists: Experts who manage and analyze complex, large-scale data structures.
In today’s data-driven world, these roles are the backbone of business decision-making. Industries ranging from e-commerce to healthcare rely on data experts to unlock value from information, and the growth of AI amplifies this reliance.
Cybersecurity in the Spotlight
Another high-growth area is information security, with demand expected to rise by 31%. As AI becomes integral to operations, protecting systems from breaches becomes more critical. Security analysts will need to adapt, leveraging AI-powered tools to predict and prevent cyber threats.
Jobs on the Decline
While some jobs are booming, others are shrinking. Clerical and secretarial roles are among the hardest hit, with bank tellers, cashiers, and data entry clerks seeing significant declines. These roles are increasingly automated, with AI handling tasks like data processing, scheduling, and customer service.
This shift underscores the need for workers to pivot toward roles requiring higher-order skills—problem-solving, strategic thinking, and technical expertise—areas where humans complement AI rather than compete with it.
A Top Priority: Training and Reskilling
Perhaps the most striking finding is how companies are responding. The report reveals that AI-related skills training is now a top priority for organizations. For companies with over 50,000 employees, it’s ranked as the number one strategic goal through 2027. Even smaller organizations recognize the need to upskill their workforce.
AI’s adoption isn’t slowing down. Nearly 75% of companies surveyed plan to integrate AI into their workflows. Of these, half believe AI will lead to job growth, while 25% predict job losses. The message is clear: adaptability is key. Workers who proactively reskill will not only remain relevant but thrive in the AI-driven workplace.
The Top 10 Growing and Declining Jobs
The World Economic Forum identifies roles on both sides of the spectrum:

These lists tell a powerful story. While AI automates repetitive and manual tasks, it fuels demand for roles requiring analytical, technical, and strategic expertise.
Next StepsUnderstanding these trends is the first step toward navigating the future job market. In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into why AI is creating more jobs than it replaces and how this transformation is impacting various industries.
3. Why AI Creates More Jobs Than It Replaces
When it comes to AI’s impact on the job market, the narrative is often polarized. Headlines warn of mass job losses, but the reality is more nuanced—and optimistic. History shows us that every technological revolution creates more jobs than it displaces. AI is no different.
Automation vs. Augmentation
The fear that AI will lead to widespread unemployment overlooks a critical point: AI doesn’t replace humans—it augments them. Automation takes over repetitive, mundane tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex, creative, and impactful responsibilities.
For instance:
In Healthcare, AI streamlines administrative duties like patient scheduling and data entry, enabling medical professionals to focus on patient care and innovation in treatment.
In Manufacturing, robots handle assembly line tasks, while humans oversee operations, troubleshoot issues, and drive innovation in production processes.
This partnership between humans and machines enhances productivity and often creates new roles that didn’t exist before.
The “Multiplier Effect” of AI
AI doesn’t just enhance existing roles; it spawns entirely new industries. Consider these examples:
AI Ethics and Regulation: As AI becomes pervasive, demand has surged for professionals who ensure ethical AI deployment, manage biases in algorithms, and navigate regulatory compliance.
AI-Powered Services: The rise of tools like ChatGPT has led to roles in conversational AI design, prompt engineering, and chatbot analytics—fields unheard of a decade ago.
Support Ecosystems: Every AI-driven system requires infrastructure, creating demand for cloud specialists, system architects, and cybersecurity professionals.
This “multiplier effect” extends to ancillary industries like training and education, where platforms like Coursera and Udemy have seen booming enrollments in AI-related courses.
Why Jobs Grow in AI-Enabled Industries
Industries that embrace AI aren’t just automating—they’re innovating. Here’s how AI drives job growth across sectors:
HealthcareAI-powered diagnostic tools have created demand for bioinformatics scientists, medical data analysts, and AI specialists in healthcare. As AI advances, roles emerge for professionals designing wearable health tech, improving drug discovery processes, and personalizing patient treatments.
Retail and E-CommerceAI-driven personalization engines require data scientists to analyze customer behavior. Automation in logistics, like AI-powered inventory management, has led to roles in supply chain optimization.
FinanceFraud detection and risk analysis powered by AI have created roles for ML engineers specializing in financial modeling. FinTech innovation is driving demand for AI-savvy engineers who can develop smarter banking solutions.
EducationAdaptive learning platforms like Khan Academy’s AI tutor are revolutionizing education. This requires experts in ed-tech product development, curriculum design for AI-enhanced tools, and data analysis to assess learning outcomes.
Skills Gaps as Opportunities
The rapid adoption of AI is outpacing the availability of skilled professionals. This skills gap creates opportunities for individuals to step into high-demand roles. Consider these areas of need:
Machine Learning Expertise: With AI systems requiring constant refinement, ML engineers are among the most sought-after professionals.
AI Ethics and Governance: The lack of professionals skilled in ensuring responsible AI deployment represents a growing opportunity.
Data Storytelling: Beyond technical analysis, businesses need professionals who can interpret AI insights and translate them into actionable strategies.
Upskilling in these areas not only future-proofs careers but positions individuals as indispensable contributors to their organizations.
AI Enhancing Human Creativity
Contrary to the belief that AI stifles creativity, it’s becoming a catalyst for human innovation. Generative AI tools like DALL-E and MidJourney empower artists, marketers, and designers to bring ideas to life faster than ever. Similarly, in coding, AI tools like GitHub Copilot assist developers by automating repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on architecture and innovation.
This symbiotic relationship demonstrates that AI amplifies human potential rather than diminishing it.
The Evolution of Workplaces
AI doesn’t just create jobs—it transforms how we work. Hybrid roles, which blend technical skills with traditional job functions, are becoming the norm. For example:
A marketing manager now needs to understand AI-driven analytics tools to optimize campaigns.
A recruiter must navigate AI-powered hiring platforms to identify and screen top candidates.
This evolution means workers must adapt, but it also broadens career paths, offering exciting new opportunities for those willing to evolve with the technology.
From Disruption to Opportunity
While automation is undoubtedly replacing certain roles, the key to thriving in an AI-driven job market is perspective. Jobs are not disappearing; they’re transforming. Workers who reskill and adapt are finding that AI expands opportunities rather than limiting them.
Take the example of data entry clerks, one of the roles most affected by automation. While traditional data entry is declining, demand for data management specialists—who oversee AI tools managing data—is on the rise. With training, these workers can pivot into higher-value roles within the same domain.
Preparing for AI-Driven Roles
To seize these opportunities, aspiring professionals should focus on building technical competencies, particularly in:
Programming languages like Python and R.
Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch for ML development.
Data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI.
At the same time, cultivating soft skills—like problem-solving, adaptability, and communication—ensures long-term success in AI-driven industries.
4. AI and Industry-Specific Job Growth
The impact of AI on industries is nothing short of transformative. It’s not merely about replacing jobs but redefining them, creating a landscape rich with opportunities across sectors. Let’s take a closer look at how AI is shaping specific industries and the types of roles it’s bringing to the forefront.
1. Tech Industry
For software engineers and data professionals, it offers an unparalleled chance to work on cutting-edge projects and redefine the future of technology.
AI and ML Specialists: These experts design and deploy machine learning models, working on problems ranging from natural language processing to recommendation systems.
DevOps with AI Focus: Professionals who integrate AI into software development lifecycles are in high demand, optimizing deployment pipelines and ensuring scalability.
AI Operations Managers: With AI systems deployed at scale, managers ensure uptime, accuracy, and ethical compliance.
The tech industry also sees the emergence of hybrid roles like AI-augmented product managers, who blend traditional product development expertise with a strong understanding of AI capabilities.
2. Healthcare
AI’s potential to revolutionize healthcare is enormous, from improving diagnostics to personalizing treatments. This disruption is creating specialized roles while enhancing the effectiveness of existing ones.
Medical Imaging Specialists: AI-powered imaging tools require professionals who can fine-tune algorithms to detect abnormalities such as tumors with exceptional accuracy.
Bioinformatics Scientists: These roles leverage AI to analyze genetic data, accelerating breakthroughs in personalized medicine and drug discovery.
Patient Data Analysts: With AI systems aggregating patient records, data analysts interpret trends and recommend interventions.
AI is also helping clinicians by reducing administrative burdens, allowing them to focus on direct patient care.
3. Finance and Banking
The financial sector has embraced AI to drive efficiency and enhance customer experiences, leading to a surge in new roles.
Fraud Detection Analysts: AI systems monitor transactions in real-time, flagging suspicious activity. Analysts interpret these alerts to strengthen defenses against financial crimes.
Quantitative Analysts with AI Expertise: These professionals combine traditional quantitative skills with AI to create predictive models for stock trading, credit risk assessment, and portfolio optimization.
Customer Personalization Experts: AI-powered tools analyze customer behavior, creating personalized financial advice and product recommendations.
These innovations are complemented by advancements in blockchain and cybersecurity, further expanding job opportunities.
4. Retail and Logistics
AI is a game-changer for retail and logistics, enhancing efficiency and transforming customer experiences.
Inventory Management Specialists: AI tools predict demand, optimize stock levels, and reduce waste, creating demand for professionals who oversee these systems.
Last-Mile Logistics Coordinators: With AI-driven route optimization, coordinators manage delivery systems for speed and cost-efficiency.
Customer Data Analysts: AI tools in e-commerce platforms track and predict consumer preferences, driving targeted marketing campaigns.
As companies like Amazon and Walmart lead the way in AI adoption, opportunities abound for professionals ready to harness these tools.
5. Education and Training
AI’s influence in education is creating a more personalized and efficient learning experience while opening up new avenues for educators and technologists.
Ed-Tech Developers: These professionals design AI-driven platforms for adaptive learning, tailoring content to individual student needs.
Curriculum Designers for AI Tools: With platforms like Duolingo and Khan Academy using AI, there’s demand for educators who can create effective AI-supported learning materials.
Data Analysts in Education: By analyzing learning outcomes and engagement data, these roles ensure educational strategies are optimized for success.
AI isn’t just transforming what students learn but how they learn, making education more accessible and impactful.
6. Manufacturing and Robotics
Manufacturing is one of the most visible beneficiaries of AI, with automation streamlining production and boosting efficiency.
Robotics Engineers: As AI-powered robots take on complex manufacturing tasks, engineers are needed to design, build, and maintain these systems.
Predictive Maintenance Specialists: AI tools monitor equipment health in real time, requiring experts to interpret data and preemptively address issues.
Digital Twin Specialists: This emerging role involves creating virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate performance and optimize processes.
These roles highlight the shift from manual labor to AI-assisted decision-making in manufacturing.
7. Energy and Environment
As sustainability becomes a global priority, AI is driving innovation in renewable energy and environmental protection.
Renewable Energy Analysts: AI tools optimize energy production from solar and wind sources, creating roles for specialists who can manage these technologies.
Environmental Data Scientists: These professionals analyze data to model climate change scenarios, helping policymakers and businesses make informed decisions.
Smart Grid Engineers: AI-driven grids balance energy supply and demand, requiring engineers to ensure seamless operations.
AI’s role in combating climate change underscores its potential to solve some of humanity’s greatest challenges.
8. Media and Entertainment
AI is revolutionizing content creation, distribution, and audience engagement in the media and entertainment industry.
Content Personalization Experts: Streaming platforms like Netflix rely on AI to recommend content, driving demand for specialists who optimize these algorithms.
Virtual Production Engineers: AI tools enable real-time editing and animation, creating opportunities in film and gaming production.
Generative AI Artists: As tools like DALL-E gain popularity, new creative roles are emerging for those who can leverage AI to produce art, music, and storytelling.
By democratizing content creation, AI is empowering creators while expanding career opportunities.
Key Takeaways Across Industries
Hybrid Roles Are the Future: AI is blending traditional job functions with technical expertise, requiring workers to upskill and adapt.
Interdisciplinary Knowledge is Key: Professionals who combine AI expertise with industry-specific knowledge are in high demand.
The Need for Continuous Learning: As AI evolves, staying updated with the latest tools and techniques is essential for long-term success.
5. The Human Factor: What AI Can’t Replace
As AI reshapes industries and workflows, one thing remains clear: machines, no matter how advanced, cannot replace the uniquely human traits that drive creativity, empathy, and critical thinking. These qualities ensure that humans remain at the heart of decision-making, innovation, and relationship-building in the workplace.
Core Human Traits That Machines Can’t Replicate
Creativity and InnovationAI excels at pattern recognition, but true creativity—the ability to produce something genuinely new and original—remains a distinctly human trait. While tools like generative AI can assist in brainstorming or prototyping, they rely on inputs derived from human ingenuity.
A designer can use AI to generate initial concepts, but the final vision and creative narrative come from their unique perspective.
In fields like scientific research, humans push the boundaries of knowledge, forming hypotheses that AI models can test but cannot originate.
Empathy and Emotional IntelligenceAI can simulate human conversation, but it lacks the capacity for genuine empathy. Emotional intelligence—understanding, interpreting, and responding to human emotions—is essential in roles like leadership, counseling, and customer service.
A therapist’s ability to connect deeply with a patient cannot be replicated by an AI chatbot, no matter how advanced.
Leaders inspire and motivate teams through empathy and trust, qualities AI cannot emulate.
Decision-Making in Complex, Unstructured EnvironmentsAI thrives in structured settings where rules and data are well-defined. However, real-world problems often involve uncertainty, ethical dilemmas, and competing priorities. Humans excel at navigating these complexities, balancing logic with intuition.
In healthcare, for example, a doctor might weigh clinical guidelines, patient history, and ethical considerations to make life-saving decisions that go beyond AI’s programmed algorithms.
In business, managers must account for organizational culture, team dynamics, and long-term goals when strategizing—factors AI cannot fully comprehend.
Relationship Building and CommunicationInterpersonal skills remain irreplaceable in fostering relationships and collaboration. Whether in sales, diplomacy, or teamwork, the ability to build trust and understand nuanced social cues is vital.
Negotiations require adaptability and emotional understanding that AI lacks.
Teams rely on leaders and peers who can resolve conflicts and foster cohesion, roles that depend on human intuition and empathy.
Generative AI and Collaboration
Generative AI, like tools that create art, write code, or draft text, has sparked concerns about automation encroaching on creative roles. However, these tools are better seen as collaborators rather than competitors. They enhance human creativity by reducing repetitive tasks and offering new ways to ideate.
In Content Creation: Writers and marketers use generative AI to draft ideas or create variations of content, freeing them to focus on strategy and storytelling.
In Design: Tools like Adobe Firefly allow graphic designers to quickly generate iterations, speeding up workflows while preserving the designer’s artistic vision.
In Software Development: Developers can rely on AI-powered assistants like GitHub Copilot to handle boilerplate code, letting them focus on architecture and problem-solving.
By leveraging these tools, professionals can amplify their output while maintaining the creative and strategic core of their work.
The Growing Value of Human-Led Roles
As AI automates repetitive tasks, the demand for roles emphasizing human interaction and judgment is increasing. These roles often require a blend of technical knowledge and soft skills, ensuring that workers bring both expertise and a personal touch to their jobs.
Leadership Roles: The ability to inspire, motivate, and manage teams is critical as workplaces become more hybrid and distributed.
Strategy and Vision: Strategic roles that envision long-term goals and align AI initiatives with broader organizational values remain exclusively human.
Client-Facing Positions: Customer success managers and relationship advisors rely on empathy and active listening to solve problems and build loyalty.
The Role of Generative AI in Creative Partnerships
Instead of replacing humans, generative AI is redefining how we approach creative work. It serves as a brainstorming partner, a drafting tool, and a catalyst for ideas, offering possibilities we might not consider.
Music and Film: AI-generated compositions and scripts provide starting points for artists, who refine and elevate these ideas to create memorable works.
Marketing Campaigns: AI tools generate multiple ad concepts, allowing marketers to test and optimize their campaigns efficiently.
Architecture and Urban Planning: AI models visualize design possibilities, enabling architects to experiment with novel layouts and structures.
These examples illustrate how humans remain the driving force behind creativity, using AI as an enhancer rather than a replacement.
Balancing AI with Ethical and Emotional Oversight
AI systems can execute tasks with incredible efficiency, but they lack an understanding of ethics, context, and cultural nuances. This underscores the importance of human oversight to ensure AI is used responsibly.
AI Ethics Teams: These professionals work to mitigate biases in AI algorithms, ensuring they align with ethical standards.
Crisis Management: Humans intervene in situations where AI may produce harmful or unintended outcomes, maintaining accountability and trust.
By emphasizing roles that combine technical knowledge with ethical considerations, organizations can build systems that serve humanity’s best interests.
Preparing for a Future Where Humans and AI Coexist
As AI adoption accelerates, professionals must focus on cultivating the skills that set them apart from machines. Here’s how workers can thrive in this new era:
Embrace Lifelong Learning: Stay ahead by continuously learning new tools and techniques, particularly those that enhance your field.
Strengthen Interpersonal Skills: Develop emotional intelligence and leadership qualities that complement technical expertise.
Seek Hybrid Opportunities: Pursue roles that combine AI proficiency with creative, ethical, or strategic responsibilities.
AI may be a transformative force, but human skills are the foundation of its success. By focusing on what makes us uniquely human, we can ensure a harmonious and productive coexistence with technology.
6. AI and Workplace Transformation
AI is not only creating new jobs but also transforming how workplaces function. By automating routine tasks, streamlining workflows, and enabling data-driven decision-making, AI is changing the dynamics of modern offices. To thrive in this evolving environment, professionals must adapt to new roles, tools, and collaborative structures.
How AI is Changing Workplace Dynamics
Automating Repetitive TasksAI is freeing employees from time-consuming, mundane tasks. In sectors like finance, healthcare, and retail, automation is driving efficiency.
Examples:
AI-powered systems can automatically process invoices, schedule meetings, and generate reports.
In healthcare, tools like transcription software streamline patient record management, allowing staff to focus on patient care.
Enhancing Decision-MakingAI enables organizations to make faster, data-driven decisions by providing real-time insights.
Case Studies:
Retailers use AI to predict trends and optimize inventory, reducing waste and maximizing profits.
Marketing teams leverage AI tools to analyze customer behavior, refining campaigns for better engagement.
Facilitating Remote and Hybrid WorkAI tools are playing a pivotal role in enabling seamless remote and hybrid work models.
Collaboration Platforms: AI-driven tools like Microsoft Teams and Slack now include features like transcription, task tracking, and meeting summaries, enhancing productivity.
Employee Monitoring and Support: AI can track employee well-being and engagement, helping managers address burnout proactively.
The integration of AI ensures that hybrid teams remain connected, efficient, and supported, regardless of physical location.
The Shift Toward Hybrid Roles
AI is blending technical and non-technical responsibilities, leading to the rise of hybrid roles. These positions require employees to combine domain expertise with an understanding of AI systems.
Marketing with AI: Marketers now need to analyze data generated by AI tools to fine-tune campaigns.
AI-Augmented Project Managers: Project managers must oversee teams using AI tools, ensuring that outputs align with business goals.
Sales and AI: Sales representatives leverage AI insights to understand customer needs, tailor pitches, and predict purchasing behaviors.
Hybrid roles not only demand new skills but also open up opportunities for employees to engage in more impactful work.
Workplace Priorities: Training and Upskilling
As AI adoption grows, companies are prioritizing workforce development to bridge skill gaps. The Future of Jobs Report 2023 reveals that training staff to work with AI and big data is among the top three priorities for businesses, with large organizations making it their number one focus.
Upskilling Programs:
Companies are investing in training programs to help employees adapt to AI-enabled workflows.
For example, Google and Amazon offer AI certifications to upskill their teams.
Cross-Functional Training:
Employees are being trained to work across departments, enabling smoother collaboration in AI-enhanced environments.
Accessible Learning Platforms:
Online platforms like Coursera and Udacity make AI education more accessible, offering courses in data science, machine learning, and AI ethics.
The Human-Machine Collaboration
AI is not replacing workers—it’s becoming a trusted collaborator. By combining the speed and precision of machines with the creativity and judgment of humans, workplaces are achieving unprecedented efficiency and innovation.
Co-Authoring with AI: Writers and researchers use AI tools to draft and refine content, accelerating the creative process.
Collaborative Problem-Solving: In fields like architecture, AI helps simulate designs, while humans decide on aesthetics and feasibility.
Continuous Feedback: AI tools analyze employee performance data, providing managers with actionable insights to enhance productivity.
This collaboration between humans and machines underscores the importance of fostering an AI-savvy workforce.
Preparing for the AI-Enhanced Workplace
Workers must adapt to AI-driven transformations by cultivating skills and mindsets that complement AI technologies.
Technical Proficiency:
Learn to use AI tools specific to your industry, such as predictive analytics platforms or automation software.
Understand the basics of machine learning and data interpretation.
Soft Skills Development:
Improve communication, teamwork, and adaptability to excel in hybrid roles.
Cultivate critical thinking to make informed decisions in AI-augmented environments.
Continuous Learning:
Stay updated with evolving AI trends and applications through workshops, webinars, and online courses.
AI’s Role in Shaping Future Workplaces
AI is not just transforming individual roles—it’s redefining organizational culture and priorities.
Diversity and Inclusion: AI can help identify and address biases in hiring, ensuring more equitable opportunities.
Sustainability: AI-driven tools are helping companies reduce energy consumption and waste, making workplaces more sustainable.
Work-Life Balance: Automation of tedious tasks allows employees to focus on meaningful work, improving overall job satisfaction.
These shifts highlight AI’s potential to create workplaces that are not only more efficient but also more human-centric.
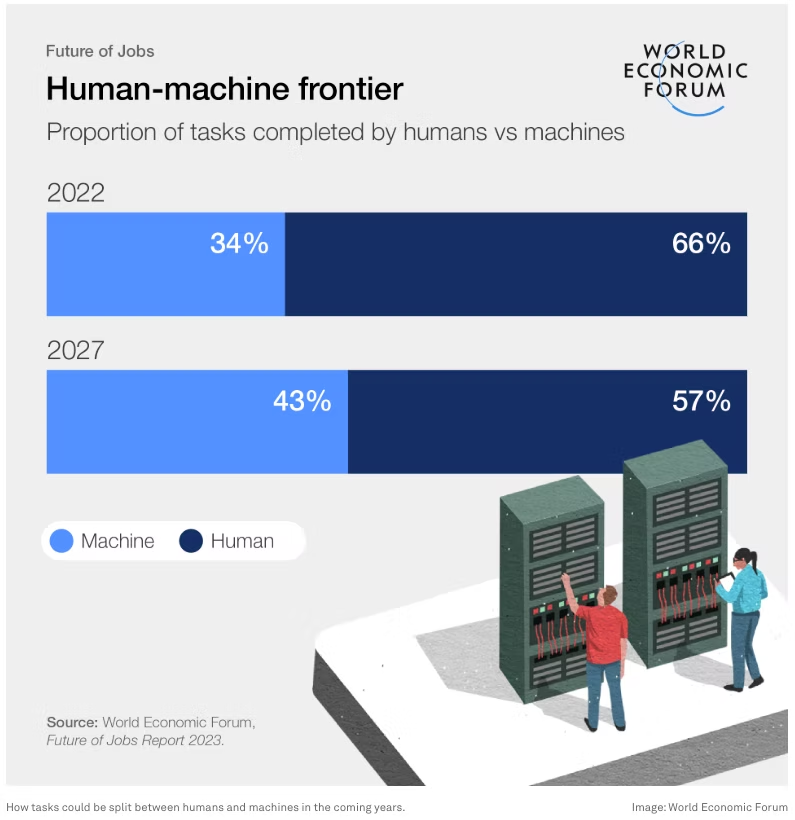
7. Preparing for an AI-Driven Career
With AI transforming industries and creating new roles, professionals need to prepare to capitalize on these opportunities. Breaking into an AI-driven career—especially in machine learning (ML)—requires a combination of technical skills, hands-on experience, and networking.
Key Skills and Tools to Master
Programming Languages
Python: The go-to language for AI and ML due to its simplicity and robust libraries (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn).
R: Essential for data analysis and visualization.
SQL: Vital for managing and querying data.
Machine Learning Frameworks
TensorFlow and PyTorch: Mastering these frameworks is crucial for developing AI models.
Keras: A user-friendly API for building deep learning models.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure are integral for deploying scalable AI solutions.
Data Visualization
Tools like Tableau and Power BI help present complex data in an understandable way, a key skill for communicating AI’s value to stakeholders.
Soft Skills
Problem-solving: Approaching AI challenges with creativity and resourcefulness.
Communication: Explaining complex AI concepts to non-technical audiences.
Certifications and Courses
Earning certifications not only enhances your skills but also demonstrates credibility to employers. Some popular programs include:
Google Professional Machine Learning Engineer
Focuses on designing and implementing ML solutions on Google Cloud.
AWS Certified Machine Learning – Specialty
Covers building, training, and deploying ML models on AWS.
Stanford’s Machine Learning Course (Andrew Ng)
A comprehensive introduction to ML concepts and algorithms.
Deep Learning Specialization (Coursera)
A deep dive into neural networks and deep learning architectures.
Building a Portfolio
A strong portfolio demonstrates your ability to solve real-world problems using AI and ML.
Capstone Projects: Build projects that showcase your expertise, such as developing a recommendation engine or training an image recognition model.
Open-Source Contributions: Collaborate on GitHub projects to showcase your coding skills and teamwork.
Competitions: Participate in platforms like Kaggle to gain experience solving industry-relevant AI problems.
Networking and Branding
Establishing a professional brand is critical for landing AI roles.
LinkedIn:
Share your projects and insights about AI trends.
Connect with industry professionals and participate in discussions.
GitHub:
Maintain an active repository of your AI projects.
Showcase clean, well-documented code.
Tech Meetups and Conferences:
Attend events to meet professionals, gain insights, and find mentorship opportunities.
AI Communities:
Join online forums like Reddit’s r/MachineLearning and participate in AI-focused Slack groups.
The Job Application Process
Target Your Resume
Highlight relevant skills, certifications, and projects.
Use quantifiable achievements to demonstrate impact, e.g., “Improved model accuracy by 15% using advanced hyperparameter tuning.”
Ace the Technical Interview
Brush up on algorithms, data structures, and problem-solving techniques.
Prepare for ML-specific questions, such as explaining algorithms or discussing your approach to handling imbalanced datasets.
Mock Interviews
Practice with peers or platforms like InterviewNode to simulate real-world scenarios and receive constructive feedback.
8. How InterviewNode Can Help You Land an ML Role
If you’re an aspiring machine learning professional, navigating the competitive landscape of top-tier tech interviews can be challenging. That’s where InterviewNode steps in.
Tailored ML Interview Preparation
At InterviewNode, we specialize in helping software engineers prepare for machine learning roles at leading companies. Our platform is designed to address your unique needs, offering:
Customized Study Plans: We identify your strengths and weaknesses to create a personalized roadmap.
Interview Simulations: Realistic mock interviews that mimic the exact scenarios you’ll encounter at companies like Google, Amazon, and OpenAI.
Skills Gap Analysis
Many candidates struggle with identifying gaps in their technical or behavioral skills.
In-Depth Feedback: After each mock interview, you’ll receive actionable insights to refine your approach.
Targeted Resources: Access curated content, from tutorials on ML algorithms to best practices for explaining complex concepts during interviews.
Real-World ML Challenges
Our platform offers industry-standard machine learning problems that test your knowledge in areas like:
Model deployment and optimization.
Handling imbalanced datasets.
Designing scalable AI solutions.
Community and Networking
InterviewNode connects you with a community of like-minded individuals, mentors, and alumni who’ve successfully transitioned into top-tier ML roles.
Discussion Forums: Collaborate and share insights with other candidates.
Success Stories: Learn from those who’ve navigated the journey you’re embarking on.
Why Choose InterviewNode?
We understand the unique challenges of preparing for ML interviews. With our data-driven approach and expert guidance, you’ll gain the confidence and skills to excel. Ready to take the next step in your career? Let InterviewNode be your partner on the journey to success.
9. Conclusion: Embracing the AI Revolution
The AI revolution isn’t a threat—it’s an opportunity. By automating routine tasks and enabling groundbreaking innovations, AI is reshaping the job market in ways that reward adaptability, creativity, and technical expertise.
The Future of Jobs Report 2023 makes one thing clear: while some roles will fade away, others are set to thrive. With a 40% increase in demand for AI and ML specialists by 2027, now is the time to upskill, embrace change, and seize the opportunities this transformation offers.
For software engineers, the path to an ML career starts with preparation. By mastering key skills, building a portfolio, and leveraging platforms like InterviewNode, you can position yourself as a top candidate in a rapidly growing field.
AI isn’t just about machines; it’s about humans working with machines to unlock potential and create a better future. Are you ready to be a part of it?






